AMBA AXI vs PCIe Protocol: A Comprehensive Comparison for VLSI Engineers
- VLSI Mentor Team

- 6 days ago
- 11 min read
In modern System-on-Chip (SoC) and computer architecture design, choosing the right interconnect protocol is crucial for achieving optimal performance, power efficiency, and system integration.
Two of the most prominent protocols in the industry are AMBA AXI (Advanced eXtensible Interface) and PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express). While both serve as high-speed data transfer mechanisms, they are designed for fundamentally different use cases and architectural contexts.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the key differences, architectural details, practical implementations, and real-world applications of both protocols.
Whether you're a VLSI design engineer, verification engineer, or student learning about on-chip and off-chip communication, this article will provide you with deep insights backed by code examples, block diagrams, and timing waveforms.
Overview and Use Cases
AMBA AXI Protocol
AMBA (Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture) is an ARM standard for on-chip communication. The AXI protocol is part of the AMBA family and is specifically designed for high-performance, high-frequency system designs.
On-chip interconnect protocol with parallel bus architecture with multiple channels.
It supports low-latency on-chip communication with burst-based & out-of-order data transactions and independent/separate read/write channels.
It is used in CPU to memory controller communication, DMA engine interfaces, High-speed peripheral interfaces (GPU, DSP), SoC internal communication fabric, and FPGA internal interconnects.

PCIe Protocol
PCIe (PCI Express) is an industry-standard serial communication protocol designed for high-speed data transfer between chips, cards, and systems.
A primarily off-chip, serial point-to-point interconnect protocol with a layered stack, packet-based communication, scalable multi-lane bandwidth, hot-plug support, and advanced power management.
It is used in Graphics card (GPU) to CPU communication, NVMe SSD interfaces, Network interface cards (NICs), External device connectivity, Server-grade interconnects, and FPGA to host PC communication.

Protocol Stack Comparison

AMBA-AXI Deep Dive
AXI Channel Architecture
AXI protocol uses five independent channels for communication:
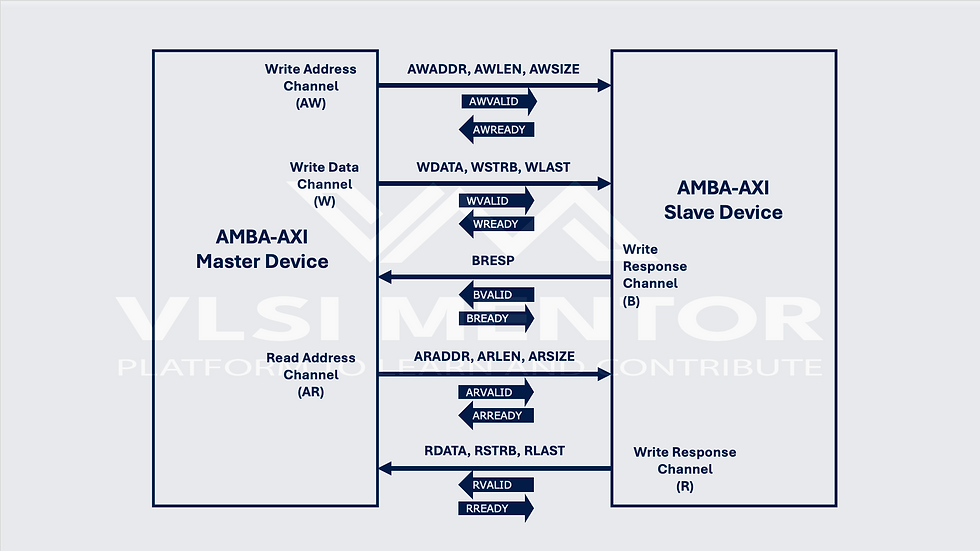
AXI Transaction Types
Single Transfer
Single Write Transaction:
- AWLEN = 0 (1 transfer)
- AWSIZE = 3'b010 (4 bytes)
- AWADDR = 0x1000 Single Read Transaction:
- ARLEN = 0 (1 transfer)
- ARSIZE = 3'b010 (4 bytes)
- ARADDR = 0x2000Burst Transfer
Burst Write Transaction:
- AWLEN = 7 (8 transfers)
- AWSIZE = 3'b011 (8 bytes)
- AWBURST = 2'b01 (INCR - incrementing)
- AWADDR = 0x1000
Addresses accessed: 0x1000, 0x1008, 0x1010, 0x1018...AXI Signal Definitions
// Write Address Channel Signals
output [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] AWADDR // Write address
output [7:0] AWLEN // Burst length (0-255)
output [2:0] AWSIZE // Burst size (bytes per beat)
output [1:0] AWBURST // Burst type (FIXED, INCR, WRAP)
output [3:0] AWID // Write transaction ID
output AWVALID // Write address valid
input AWREADY // Write address ready
// Write Data Channel Signals
output [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] WDATA // Write data
output [DATA_WIDTH/8-1:0] WSTRB // Write strobes (byte enables)
output WLAST // Write last transfer
output WVALID // Write data valid
input WREADY // Write data ready
// Write Response Channel Signals
input [3:0] BID // Response ID
input [1:0] BRESP // Response (OKAY, EXOKAY, SLVERR, DECERR)
input BVALID // Write response valid
output BREADY // Response ready
// Read Address Channel Signals
output [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] ARADDR // Read address
output [7:0] ARLEN // Burst length
output [2:0] ARSIZE // Burst size
output [1:0] ARBURST // Burst type
output [3:0] ARID // Read transaction ID
output ARVALID // Read address valid
input ARREADY // Read address ready
// Read Data Channel Signals
input [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] RDATA // Read data
input [3:0] RID // Read ID
input [1:0] RRESP // Read response
input RLAST // Read last transfer
input RVALID // Read data valid
output RREADY // Read readyPCIe Protocol Deep Dive
PCIe Layered Architecture

PCIe Transaction Layer Packet (TLP) Format

Configuration Space Header (Type 0):
00h: Device ID (16b) | Vendor ID (16b)
04h: Status (16b) | Command (16b)
08h: Class Code (24b) | Revision ID (8b)
0Ch: BIST | Header | Latency | Cache Line
10h: Base Address Register 0 (BAR0)
14h: Base Address Register 1 (BAR1)
18h: Base Address Register 2 (BAR2)
1Ch: Base Address Register 3 (BAR3)
20h: Base Address Register 4 (BAR4)
24h: Base Address Register 5 (BAR5)
28h: Cardbus CIS Pointer
2Ch: Subsystem ID | Subsystem Vendor ID
30h: Expansion ROM Base Address
34h: Reserved | Capabilities Pointer
38h: Reserved
3Ch: Max_Lat | Min_Gnt | Int Pin | Int Line
40h+: Extended CapabilitiesKey Differences

Verilog Implementation Sample
AXI Master Design
module axi_master_write #(
parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 32,
parameter DATA_WIDTH = 32,
parameter ID_WIDTH = 4
)(
input wire aclk,
input wire aresetn,
// User interface
input wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] user_write_addr,
input wire [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] user_write_data,
input wire user_write_start,
output reg user_write_done,
// AXI Write Address Channel
output reg [ID_WIDTH-1:0] m_axi_awid,
output reg [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] m_axi_awaddr,
output reg [7:0] m_axi_awlen, // Burst length
output reg [2:0] m_axi_awsize, // Burst size
output reg [1:0] m_axi_awburst, // Burst type
output reg m_axi_awvalid,
input wire m_axi_awready,
// AXI Write Data Channel
output reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] m_axi_wdata,
output reg [(DATA_WIDTH/8)-1:0] m_axi_wstrb,
output reg m_axi_wlast,
output reg m_axi_wvalid,
input wire m_axi_wready,
// AXI Write Response Channel
input wire [ID_WIDTH-1:0] m_axi_bid,
input wire [1:0] m_axi_bresp,
input wire m_axi_bvalid,
output reg m_axi_bready
);
// State machine states
localparam IDLE = 3'b000;
localparam WRITE_ADDR = 3'b001;
localparam WRITE_DATA = 3'b010;
localparam WRITE_RESP = 3'b011;
localparam DONE = 3'b100;
reg [2:0] state, next_state;
reg [ID_WIDTH-1:0] transaction_id;
// State machine sequential logic
always @(posedge aclk or negedge aresetn) begin
if (!aresetn) begin
state <= IDLE;
transaction_id <= 0;
end else begin
state <= next_state;
if (state == DONE) begin
transaction_id <= transaction_id + 1;
end
end
end
// State machine combinational logic
always @(*) begin
next_state = state;
case (state)
IDLE: begin
if (user_write_start) begin
next_state = WRITE_ADDR;
end
end
WRITE_ADDR: begin
if (m_axi_awvalid && m_axi_awready) begin
next_state = WRITE_DATA;
end
end
WRITE_DATA: begin
if (m_axi_wvalid && m_axi_wready && m_axi_wlast) begin
next_state = WRITE_RESP;
end
end
WRITE_RESP: begin
if (m_axi_bvalid && m_axi_bready) begin
next_state = DONE;
end
end
DONE: begin
next_state = IDLE;
end
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
// AXI signal generation
always @(posedge aclk or negedge aresetn) begin
if (!aresetn) begin
m_axi_awid <= 0;
m_axi_awaddr <= 0;
m_axi_awlen <= 0;
m_axi_awsize <= 3'b010; // 4 bytes
m_axi_awburst <= 2'b01; // INCR
m_axi_awvalid <= 1'b0;
m_axi_wdata <= 0;
m_axi_wstrb <= {(DATA_WIDTH/8){1'b1}};
m_axi_wlast <= 1'b0;
m_axi_wvalid <= 1'b0;
m_axi_bready <= 1'b0;
user_write_done <= 1'b0;
end else begin
// Default values
user_write_done <= 1'b0;
case (state)
IDLE: begin
if (user_write_start) begin
m_axi_awid <= transaction_id;
m_axi_awaddr <= user_write_addr;
m_axi_awlen <= 8'h00; // Single beat
m_axi_awvalid <= 1'b1;
m_axi_wdata <= user_write_data;
m_axi_wlast <= 1'b1;
end
end
WRITE_ADDR: begin
if (m_axi_awready) begin
m_axi_awvalid <= 1'b0;
end
end
WRITE_DATA: begin
m_axi_wvalid <= 1'b1;
if (m_axi_wready) begin
m_axi_wvalid <= 1'b0;
m_axi_bready <= 1'b1;
end
end
WRITE_RESP: begin
if (m_axi_bvalid) begin
m_axi_bready <= 1'b0;
if (m_axi_bresp == 2'b00) begin // OKAY response
user_write_done <= 1'b1;
end
end
end
DONE: begin
// Transaction complete
end
endcase
end
end
endmoduleAXI Slave Design
module axi_slave_memory #(
parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 32,
parameter DATA_WIDTH = 32,
parameter MEM_SIZE = 1024 // Number of 32-bit words
)(
input wire aclk,
input wire aresetn,
// AXI Write Address Channel
input wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] s_axi_awaddr,
input wire s_axi_awvalid,
output reg s_axi_awready,
// AXI Write Data Channel
input wire [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] s_axi_wdata,
input wire [(DATA_WIDTH/8)-1:0] s_axi_wstrb,
input wire s_axi_wvalid,
output reg s_axi_wready,
// AXI Write Response Channel
output reg [1:0] s_axi_bresp,
output reg s_axi_bvalid,
input wire s_axi_bready,
// AXI Read Address Channel
input wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] s_axi_araddr,
input wire s_axi_arvalid,
output reg s_axi_arready,
// AXI Read Data Channel
output reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] s_axi_rdata,
output reg [1:0] s_axi_rresp,
output reg s_axi_rvalid,
input wire s_axi_rready
);
// Memory array
reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] memory [0:MEM_SIZE-1];
// Internal registers
reg [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] write_addr_reg;
reg [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] read_addr_reg;
// Response codes
localparam RESP_OKAY = 2'b00;
localparam RESP_EXOKAY = 2'b01;
localparam RESP_SLVERR = 2'b10;
localparam RESP_DECERR = 2'b11;
// Write address channel
always @(posedge aclk or negedge aresetn) begin
if (!aresetn) begin
s_axi_awready <= 1'b0;
write_addr_reg <= 0;
end else begin
if (s_axi_awvalid && !s_axi_awready) begin
write_addr_reg <= s_axi_awaddr;
s_axi_awready <= 1'b1;
end else begin
s_axi_awready <= 1'b0;
end
end
end
// Write data channel and memory write
always @(posedge aclk or negedge aresetn) begin
if (!aresetn) begin
s_axi_wready <= 1'b0;
s_axi_bvalid <= 1'b0;
s_axi_bresp <= RESP_OKAY;
end else begin
// Write data handling
if (s_axi_wvalid && !s_axi_wready) begin
// Perform memory write with byte enables
if (write_addr_reg[ADDR_WIDTH-1:$clog2(MEM_SIZE)+2] == 0)
begin
// Valid address range
for (int i = 0; i < DATA_WIDTH/8; i++) begin
if (s_axi_wstrb[i]) begin
memory[write_addr_reg[$clog2(MEM_SIZE)+1:2]][i*8 +: 8]
<= s_axi_wdata[i*8 +: 8];
end
end
s_axi_bresp <= RESP_OKAY;
end else begin
s_axi_bresp <= RESP_DECERR; // Address decode error
end
s_axi_wready <= 1'b1;
s_axi_bvalid <= 1'b1;
end else begin
s_axi_wready <= 1'b0;
// Clear response when accepted
if (s_axi_bvalid && s_axi_bready) begin
s_axi_bvalid <= 1'b0;
end
end
end
end
// Read address channel
always @(posedge aclk or negedge aresetn) begin
if (!aresetn) begin
s_axi_arready <= 1'b0;
read_addr_reg <= 0;
end else begin
if (s_axi_arvalid && !s_axi_arready) begin
read_addr_reg <= s_axi_araddr;
s_axi_arready <= 1'b1;
end else begin
s_axi_arready <= 1'b0;
end
end
end
// Read data channel
always @(posedge aclk or negedge aresetn) begin
if (!aresetn) begin
s_axi_rdata <= 0;
s_axi_rresp <= RESP_OKAY;
s_axi_rvalid <= 1'b0;
end else begin
if (s_axi_arready) begin
// Perform memory read
if (read_addr_reg[ADDR_WIDTH-1:$clog2(MEM_SIZE)+2] == 0) begin
s_axi_rdata <= memory[read_addr_reg[$clog2(MEM_SIZE)+1:2]];
s_axi_rresp <= RESP_OKAY;
end else begin
s_axi_rdata <= 32'hDEADBEEF; // Error pattern
s_axi_rresp <= RESP_DECERR;
end
s_axi_rvalid <= 1'b1;
end else if (s_axi_rvalid && s_axi_rready) begin
s_axi_rvalid <= 1'b0;
end
end
end
endmodulePCIe Transaction Layer Interface Example
module pcie_tlp_generator #(
parameter DATA_WIDTH = 128,
parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 64
)(
input wire user_clk,
input wire user_reset,
// User memory write request interface
input wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] mem_write_addr,
input wire [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] mem_write_data,
input wire [31:0] mem_write_length, // In DWORDs
input wire mem_write_start,
output reg mem_write_done,
// User memory read request interface
input wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] mem_read_addr,
input wire [31:0] mem_read_length, // In DWORDs
input wire mem_read_start,
output reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] mem_read_data,
output reg mem_read_valid,
// PCIe TLP Transmit Interface (simplified)
output reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] tx_tlp_data,
output reg tx_tlp_valid,
output reg tx_tlp_sop, // Start of packet
output reg tx_tlp_eop, // End of packet
input wire tx_tlp_ready,
// PCIe TLP Receive Interface (simplified)
input wire [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] rx_tlp_data,
input wire rx_tlp_valid,
input wire rx_tlp_sop,
input wire rx_tlp_eop,
// PCIe Configuration
input wire [15:0] requester_id, // Bus:Dev:Func
input wire [7:0] max_payload_size, // In DWORDs
input wire [7:0] max_read_request // In DWORDs
);
// TLP Format and Type definitions
localparam FMT_3DW_NO_DATA = 3'b000;
localparam FMT_4DW_NO_DATA = 3'b001;
localparam FMT_3DW_WITH_DATA = 3'b010;
localparam FMT_4DW_WITH_DATA = 3'b011;
localparam TYPE_MEM_READ = 5'b00000;
localparam TYPE_MEM_WRITE = 5'b00000;
localparam TYPE_COMPLETION = 5'b01010;
// State machine
localparam IDLE = 3'b000;
localparam GEN_MEM_WRITE_HDR = 3'b001;
localparam GEN_MEM_WRITE_DATA = 3'b010;
localparam GEN_MEM_READ_HDR = 3'b011;
localparam WAIT_COMPLETION = 3'b100;
localparam DONE = 3'b101;
reg [2:0] state, next_state;
reg [7:0] tlp_tag;
reg [9:0] data_word_count;
reg [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] current_addr;
// TLP Header fields
reg [2:0] tlp_fmt;
reg [4:0] tlp_type;
reg [2:0] tlp_tc; // Traffic class
reg [9:0] tlp_length; // In DWORDs
reg [15:0] tlp_req_id;
reg [7:0] tlp_tag_id;
reg [3:0] tlp_first_be;
reg [3:0] tlp_last_be;
// State machine
always @(posedge user_clk or posedge user_reset) begin
if (user_reset) begin
state <= IDLE;
tlp_tag <= 8'h00;
end else begin
state <= next_state;
if (state == DONE) begin
tlp_tag <= tlp_tag + 1;
end
end
end
always @(*) begin
next_state = state;
case (state)
IDLE: begin
if (mem_write_start) begin
next_state = GEN_MEM_WRITE_HDR;
end else if (mem_read_start) begin
next_state = GEN_MEM_READ_HDR;
end
end
GEN_MEM_WRITE_HDR: begin
if (tx_tlp_ready) begin
next_state = GEN_MEM_WRITE_DATA;
end
end
GEN_MEM_WRITE_DATA: begin
if (tx_tlp_ready && data_word_count == tlp_length)
begin
next_state = DONE;
end
end
GEN_MEM_READ_HDR: begin
if (tx_tlp_ready) begin
next_state = WAIT_COMPLETION;
end
end
WAIT_COMPLETION: begin
if (rx_tlp_valid && rx_tlp_eop) begin
next_state = DONE;
end
end
DONE: begin
next_state = IDLE;
end
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
// TLP generation logic
always @(posedge user_clk or posedge user_reset) begin
if (user_reset) begin
tx_tlp_data <= 0;
tx_tlp_valid <= 1'b0;
tx_tlp_sop <= 1'b0;
tx_tlp_eop <= 1'b0;
data_word_count <= 10'h0;
mem_write_done <= 1'b0;
current_addr <= 0;
tlp_fmt <= FMT_3DW_NO_DATA;
tlp_type <= TYPE_MEM_READ;
tlp_tc <= 3'b000;
tlp_length <= 10'h001;
tlp_req_id <= 16'h0000;
tlp_first_be <= 4'hF;
tlp_last_be <= 4'hF;
end else begin
mem_write_done <= 1'b0;
case (state)
IDLE: begin
tx_tlp_valid <= 1'b0;
data_word_count <= 10'h0;
if (mem_write_start) begin
current_addr <= mem_write_addr;
tlp_length <= mem_write_length[9:0];
tlp_req_id <= requester_id;
tlp_tag_id <= tlp_tag;
// Determine format based on address size
if (mem_write_addr[63:32] == 32'h0) begin
tlp_fmt <= FMT_3DW_WITH_DATA;
end else begin
tlp_fmt <= FMT_4DW_WITH_DATA;
end
tlp_type <= TYPE_MEM_WRITE;
end else if (mem_read_start) begin
current_addr <= mem_read_addr;
tlp_length <= mem_read_length[9:0];
tlp_req_id <= requester_id;
tlp_tag_id <= tlp_tag;
if (mem_read_addr[63:32] == 32'h0) begin
tlp_fmt <= FMT_3DW_NO_DATA;
end else begin
tlp_fmt <= FMT_4DW_NO_DATA;
end
tlp_type <= TYPE_MEM_READ;
end
end
GEN_MEM_WRITE_HDR: begin
if (tx_tlp_ready) begin
// Generate TLP header for memory write
// Format: [127:0] = {DW3, DW2, DW1, DW0}
// DW0: Fmt | Type | R | TC | R | Attr | R | TH | TD | EP | Attr | AT | Length
tx_tlp_data[127:120] <= {tlp_fmt, 1'b0, tlp_type[4:1]};
tx_tlp_data[119:112] <= {tlp_type[0], 1'b0, tlp_tc, 3'b000};
tx_tlp_data[111:96] <= {6'b000000, tlp_length};
// DW1: Requester ID | Tag | Last DW BE | First DW BE
tx_tlp_data[95:64] <= {tlp_req_id, tlp_tag_id, tlp_last_be, tlp_first_be};
// DW2: Address [31:2] | Reserved
tx_tlp_data[63:32] <= {current_addr[31:2], 2'b00};
// DW3: Address [63:32] (for 64-bit addressing)
if (tlp_fmt == FMT_4DW_WITH_DATA) begin
tx_tlp_data[31:0] <= current_addr[63:32];
end else begin
tx_tlp_data[31:0] <= 32'h00000000;
end
tx_tlp_valid <= 1'b1;
tx_tlp_sop <= 1'b1;
tx_tlp_eop <= 1'b0;
end
end
GEN_MEM_WRITE_DATA: begin
tx_tlp_sop <= 1'b0;
if (tx_tlp_ready) begin
// Send data payload
tx_tlp_data <= mem_write_data;
tx_tlp_valid <= 1'b1;
data_word_count <= data_word_count + (DATA_WIDTH/32);
// Check if this is the last data transfer
if (data_word_count + (DATA_WIDTH/32) >= tlp_length)
begin
tx_tlp_eop <= 1'b1;
mem_write_done <= 1'b1;
end
end
end
GEN_MEM_READ_HDR: begin
if (tx_tlp_ready) begin
// Generate TLP header for memory read
tx_tlp_data[127:120] <= {tlp_fmt, 1'b0, tlp_type[4:1]};
tx_tlp_data[119:112] <= {tlp_type[0], 1'b0, tlp_tc, 3'b000};
tx_tlp_data[111:96] <= {6'b000000, tlp_length};
tx_tlp_data[95:64] <= {tlp_req_id, tlp_tag_id, tlp_last_be, tlp_first_be};
tx_tlp_data[63:32] <= {current_addr[31:2], 2'b00};
if (tlp_fmt == FMT_4DW_NO_DATA) begin
tx_tlp_data[31:0] <= current_addr[63:32];
end
tx_tlp_valid <= 1'b1;
tx_tlp_sop <= 1'b1;
tx_tlp_eop <= 1'b1; // Read request has no data
end
end
WAIT_COMPLETION: begin
tx_tlp_valid <= 1'b0;
tx_tlp_sop <= 1'b0;
tx_tlp_eop <= 1'b0;
// Receive completion TLP with data
if (rx_tlp_valid) begin
if (rx_tlp_sop) begin
// Parse completion header
data_word_count <= 10'h0;
end else begin
// Receive data
mem_read_data <= rx_tlp_data;
mem_read_valid <= 1'b1;
data_word_count <= data_word_count +
(DATA_WIDTH/32);
end
end else begin
mem_read_valid <= 1'b0;
end
end
DONE: begin
tx_tlp_valid <= 1'b0;
mem_read_valid <= 1'b0;
end
endcase
end
end
endmoduleTiming Diagrams and Waveforms
AXI Write Transaction Timing Diagram

AXI Burst Write Transaction

Real World Applications
High-Performance Computing SoC (AXI)

Data Center Server with PCIe (Real Example)




![VHDL ARTICLE - [Hindi]](https://static.wixstatic.com/media/f904f2_fa60afde1c67401d9d7af02749d13636~mv2.png/v1/fill/w_654,h_990,al_c,q_90,enc_avif,quality_auto/f904f2_fa60afde1c67401d9d7af02749d13636~mv2.png)
Comments