10.4. Verilog Bitwise Operators: Bit-Level Logic Operations
10.4.1. Introduction
Bitwise operators are the foundation of digital logic, performing operations on individual bits of operands. Unlike logical operators that return a single Boolean result, bitwise operators return a result with the same width as the operands, making them essential for bit manipulation, masking, flag management, and low-level hardware control.
Every bitwise operation directly maps to logic gates in hardware, making them extremely efficient. At VLSI Mentor, we emphasize that understanding bitwise operators is crucial for writing efficient RTL code that translates cleanly to hardware.
10.4.2. Bitwise Operators Overview

Key Concept: Each bit position is operated on independently.
10.4.3. Truth Tables
Bitwise AND (&)
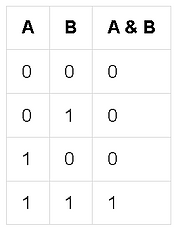
Use: Masking, clearing bits, extracting fields
Bitwise OR (|)

Use: Setting bits, combining flags
Bitwise XOR (^)

Use: Toggling bits, parity, comparison
Bitwise XNOR (~^)

Use: Equality checking per bit
Bitwise NOT (~)

Use: Inversion, one's complement
10.4.4. Bitwise AND (&) - Detailed Examples
Masking Operations
Verilog
Hardware Mapping
Verilog
Examples
10.4.5. Bitwise OR (|) - Detailed Examples
Setting Bits
Verilog
10.4.6. Bitwise XOR (^) - Detailed Examples
Toggling and Comparison
Verilog
10.4.7. Bitwise NOT (~) - One's Complement
Verilog
10.4.8. Practical Applications
Application 1: Bit Field Extraction
Verilog
Application 2: Flag Register Manager
Verilog
Application 3: Gray Code Converter
Verilog
Application 4: Parity Generator
Verilog
Application 5: Bit Manipulation Utilities
Verilog
10.4.9. Common Use Cases
1. Masking (AND)
wire [7:0] lower_nibble = data & 8'h0F;
wire [7:0] upper_nibble = data & 8'hF0;
2. Setting Bits (OR)
wire [7:0] with_bit5_set = data | 8'h20;
3. Clearing Bits (AND with NOT)
wire [7:0] with_bit5_clear = data & ~8'h20;
4. Toggling Bits (XOR)
wire [7:0] with_bit5_toggled = data ^ 8'h20;
5. Checking Bits (AND)
wire bit5_is_set = (data & 8'h20) != 0;
10.4.10. Bitwise vs Logical vs Reduction
Critical Differences
Verilog
10.4.11. Hardware Efficiency
Bitwise operators are extremely efficient:
- Each operation → One gate per bit
- No carry propagation (unlike arithmetic)
- Very fast (single gate delay)
- Low power consumption
- Direct mapping to hardware
Verilog
10.4.12. Common Pitfalls
Pitfall 1: Confusing Bitwise with Logical
Verilog
Pitfall 2: Forgetting NOT for Clearing
Verilog
Pitfall 3: Width Mismatches
Verilog
Best Practices
✅ Use for bit manipulation: Masking, setting, clearing, toggling
✅ Very hardware efficient: Direct gate mapping
✅ Document bit positions: Use comments or constants
✅ Use named masks: `MASK_ENABLE = 8'h01`
❌ Don't confuse with logical: Different purposes
❌ Don't use for conditionals: Use logical operators
